Rainwater Harvesting
Rainwater harvesting is one of the most promising alternatives for supplying water in the face of increasing water scarcity and escalating demand.
Rainwater harvesting is a technology used to collect, convey, and store rain from relatively clean surfaces such as a roof for later use. This is water that would otherwise have gone down the drainage system or into the ground. The water is generally stored in a rainwater tank or directed into mechanisms that can recharge groundwater. Rainwater harvesting can provide water for human consumption, reduce water bills, and lessen the need to build reservoirs which may require the use of valuable land.
Rainwater Harvesting Advantages
Rainwater harvesting systems are simple to install, operate, and maintain. It is convenient as it provides water at the point of consumption and operating costs are negligible. Water collected from the roof catchment is available for use in potable (per local approval) and non-potable applications such as toilet and/or urinal flushing, laundries, mechanical systems, custodial uses, and site irrigation. Since rainwater is collected using existing structures, i.e., the roof, it has few negative environmental impacts.
RWH Benefits:
-
The pressures on water supplies, the greater environmental impact associated with new projects, as well as deteriorating water quality in reservoirs already constructed, constrain the ability of communities to meet the demand for freshwater from traditional sources. Rainwater harvesting presents an opportunity for self-reliance and sustainability.
-
Once installed this is a free system which means savings on utility bills such as electricity and water.
-
As the increase demand for water grows this has led to a shortage of water especially in summer months, having your own RWH system means less dependence on other supplies.
-
Rainwater is free from most pollutants as well as salts, minerals and other man-made contaminants which means it is great for irrigation, animals and plants.
Building A RWH System
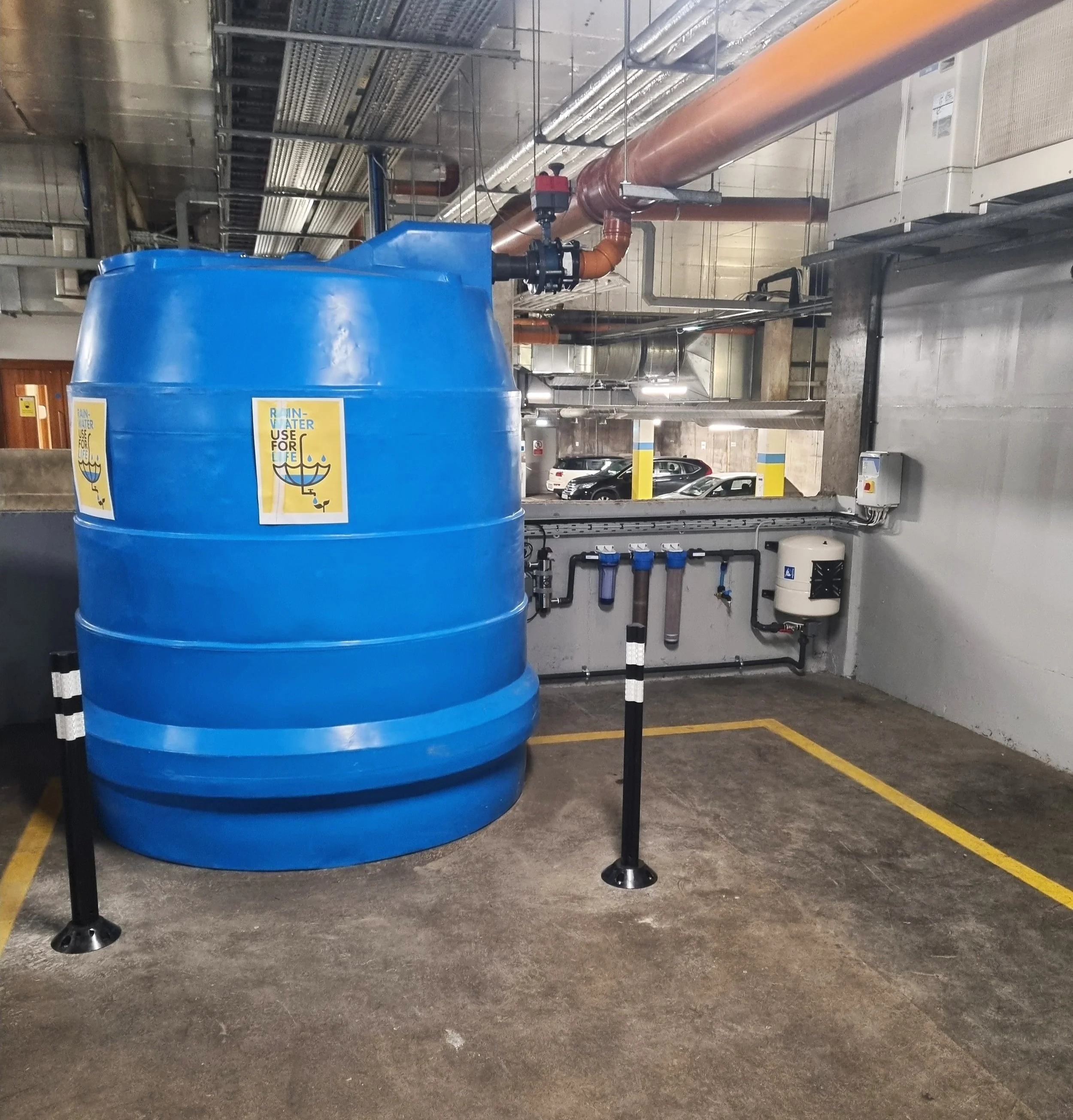
A rainwater harvesting system consists of a water tank and a harvesting kit designed to collect, filter, and pump rainwater.
Step 1 - Rainwater filter diverter
Rainwater falls from the rooftop into the guttering and through the filter which removes debris before it’s stored in the tank.
Step 2 - Calmed inlet
The diverted water runs down a pipe to the bottom of the tank where it’s released through the calmed inlet. This process oxygenates the existing water which prevents it from stagnating.
Step 3 - Overflow siphon
When the tank reaches maximum capacity the overflow siphon diverts the excess water to drainage. This process also removes pollen from the water surface to keep it clean.
Step 4 - Submersible pump
Where required a submersible pump directs the water from the bottom of the tank to the desired output.
Step 5 - Direct or Gravity
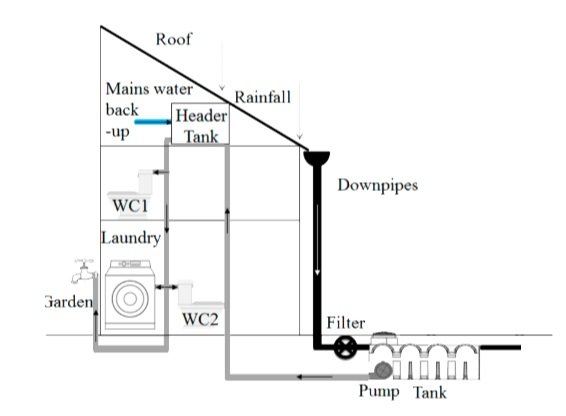
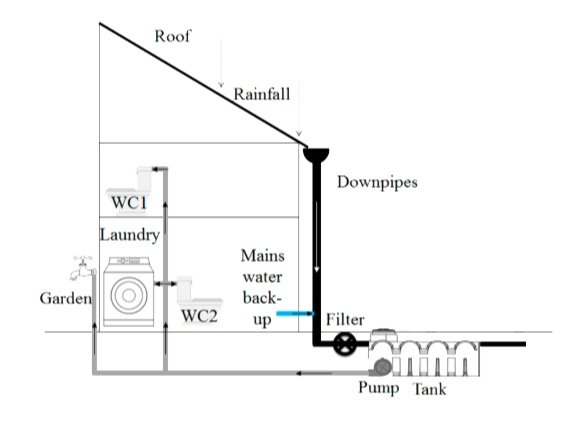
In a direct feed system, the pressure-sensitive pump in the underground tank supplies rainwater straight to appliances in the house or for use in the garden. The pump operates whenever water is requested. In a gravity-fed system, rainwater is pumped from the underground storage tank to a smart header tank. This feeds the rainwater by gravity to where it is needed. Both units are connected to a mains backup system.
Gravity Feed
Direct Feed